In a separate post I explained what SEO is and how it is done on a website level. In the same post I explained how links are created. I recommend you read that entire post first, before reading on this one. In other words: it is understood that you already know what alt and meta tags are and how to implement them, as well as how to create hyperlinks properly. This post deals primarily with the terms backlinks and domain authority and their effect on SEO and search engine website ranking (suppose this last point is the reason for your reading this post).
Disclaimer: I am by no means a SEO expert (or “ninja”, as it is popular these days), nor claim to be one. All the info provided here is “to the best of my knowledge (and experience)”.
Contents:
- Domain authority
1.1. Domain versus website
1.2. What is domain authority? - Internal and external links
- Backlinks
3.1. Hyperlink anchor text
3.2. Nofollow and do follow backlinks - 301 redirections (permanent) and SEO
- Common SEO mistakes
5.1. Too much worrying about “the keywords”
5.2. Backlink spaming
5.3. Buying backlinks, website directory listings - Conclusion and sources
1. Domain authority
In order to understand the whole backlink process, even before explaining what backlinks are, one must first understand the term: “domain authority”.
1.1. Domain versus website
In a separate post I explained what domain and sub-domain are. This website is at:
https://io.bikegremlin.com
that is io. subdomain of bikegremlin.com domain, using https: protocol only (SSL/TLS encryption).
So even though terms are overlapping to a degree, a website is not the same as a domain. One domain can host several websites at different addresses and/or sub-domains. For example, some companies often use theirdomain.com/blog for their company blog website. Others use blog.theirdomain.com.
Website, or websites (if there are several on a domain) contributes to domains authority – positively, if they are good, or negatively, if they suck.
1.2. What is domain authority?
If you are reading this, you must be working on a website, so are surely familiar with websites (and domains) like Google.com, or WordPress.org. These two domains are highly regarded in their own branches. Cyclists are surely also familiar with sheldonbrown.com (in addition to bike.bikegremlin.com 🙂 ). But, have you heard of “Killa’s Garage” website? Hat of to you if the answer is yes. Killa’s Garage is a very good cycling website that deals with some less discussed mechanical related topics – very well written, I love it.
Are you already guessing what domain authority is? The more well known and highly regarded a website is, the more domain authority it brings to its host domain.
How is website quality assessed? Several things affect the ranking:
- Content quality – how well it describes the topic it deals with. By this I don’t only mean text and pictures. Website should also be fast, secure and well visually designed. The entire visitor experience matters.
- Quality of links to the content – are the pages that link to the content also of high quality and dealing with a similar topic. I can’t just post a link to a fashion blog in the middle of this text – it would be a complete nonsense, I’d even consider it a spam. Such are above given cycling related links, except that I used them for a good reason here – as an example (not being able to think of a better one, hope you won’t mind).
- Domain authority of websites that link to the content.
- Number of links to the content – link quality and domain authority of linking websites are more important, but a greater number of links certainly helps.
Domain authority is like respect, or trust: it takes a lot of time and effort to build it, while one mistake can ruin it. That is why it’s important to keep your content with high quality, to choose good quality hosting and make sure your website is secure and well optimized (fast).
It is usually expressed using a number from 1 to 100. For example, google.com domain authority is over 95, while bikegremlin.com varies from 15 to 30, depending on the authority checker tool used. I’ll use this domain rank checking tool as a reference, then check in a few years time to see how it fares. 🙂
2. Internal and external links
Internal links of a website are those that point to other pages on the same website.
External links point to pages of other websites.
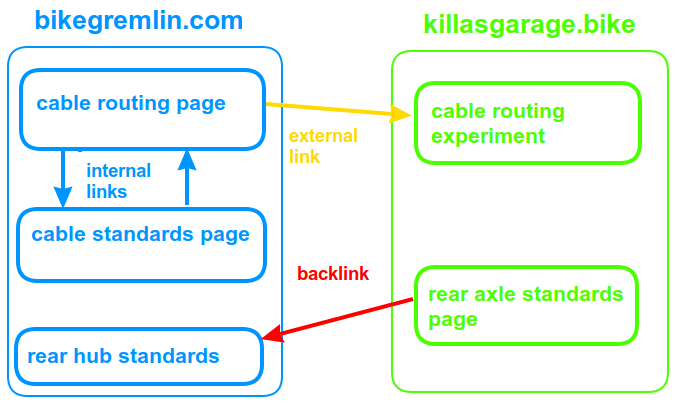
In this post’s introduction and in chapter 1.1. I have already created some internal links, ie. links to this same website’s other pages. Principles I stick to are the following:
- If I’m using a term that isn’t explained (doesn’t go for things that are considered as general knowledge) and adding an explanation on the same page would make it too long, I create a separate post explaining it and just link to it appropriately.
- When there are pages with related topic, something I think the readers would be interested in, I also often link to that.
- If I don’t have the content I’m looking for on my website, or I find something exceptionally well explained on another website of good quality (fast, secure and well designed), I will link to that content, which is not an internal link, but an external link – that is, I am creating backlinks to that website – which leads us to the next chapter.
Practical example:
Say you are selling a email hosting service. You want people to find your website when googling: “email hosting”. What would I do?
- I’d first write a post explaining all the available options (providers), including my service. With a brief explanation of each offer – price, general pros and cons.
- I’d make a series of posts explaining each provider in more detail.
- I’d write how to set up website for using an external email service, with both cPanel and DirectAdmin.
- Separate post explaining the pros and cons of using a separate mail service, instead of that offered by most shared hosting providers (included in the price, “free”).
- An article about my offer – with objectively noted pros and cons, for which use case is it a better choice than the competition.
- Next up would be knowledge base, with explanations how to setup my service with Cloudflare, cPanel and DirectAdmin DNS settings.
- Each often asked question by clients is a topic for a separate article.
- Every problem I had to overcome and every mistake I’ve made are topics for articles, with explanation of solutions and what was done to prevent it from re-occuring.
- The entire time, each page should link to other pages where it is appropriate.
3. Backlinks
Backlink is a link from another website to your website.
When a website from a domain of high authority links to a page on your website that deals with a similar topic, then your domain’s authority grows and your website becomes more widely recognized.
Domain authority, that greatly affects ranking of your website pages, can be increased in the following ways:
- Creating good content, as explained in chapter 1.2.
- Making good internal links.
- Good quality backlinks.
Good quality content, if there is enough of it and you make good internal links, will come on top sooner, or later. Still, until that happens, what can you do? This leads us to the only aspect that one can’t directly control: backlinks.
Of course, once you’re on google’s first page, with good quality content, people will share it and link to it from their websites, thus increasing your domain’s authority and search result page positioning of your pages (SERP – Search Engine Results Page). But what to do with a website and domain that are still not well known?
Provided you have good quality content (it boils down to that, whichever way you look at it). Follow social network groups and forums that deal with the theme your website is about. Get well acquainted with the atmosphere of each, contribute constructively to discussions. Once you have enough reputation and credibility that your advice is taken as good, you will be in a position to post a link to your page instead of writing a reply. If the page really deals with the topic at hand and the content really is of good quality.
Don’t spam. If you are not 100% certain that your page really is the best answer, only saving you time from re-typing the same over again, then better to not post any links. After several great links that really help, people will realize your website is a good source of information and start sharing those links among themselves and on the networks.
Making an account for your brand on every large social network doesn’t provide good quality backlinks in and of itself, but it helps by signalizing to search engines that say: “this particular Instagram account” is related to your domain. So any future posting you make (if you take the time to participate) will also count as your domain activity (not even as close as posting pages on your website, but it does help).
Getting to know other webmasters and discussing topics with them can also help. As long as it is genuine exchange of ideas and thoughts. On more than one occasion I have consulted other experts about a certain topic in their published content, stating that I want to write in more detail about it. Ending up with a backlink to my website looking like “this is explained in more detail in Bike Gremlin’s post abcdefg”. And vice-versa, when I have linked to other websites.
This is not something to be expected, nor taken for granted, but it is often the result of similar minds coming together (Internet bridges the gaps of borders, oceans and time zones – connecting people and offering the entire human knowledge a click of a button away).
Likewise, this isn’t about reciprocity. Once you figure how cool it is to have great content you worked hard on making linked and praised for, remember it. And do the same when you come across great content. Regardless of whether that website owner had linked to your content as well, or not. Spread the knowledge, good quality and good energy – it pays back tenflold, in ways you often can’t even imagine.
I must again stress the importance of the content quality – this goes for both your website and the website you got a backlink from. For example: if you have a cycling website, then another good quality cycling site, that links to your from the middle of a good quality page, carries a lot more weight, than getting linked from a fashion blog, for a simple reason: who’s advice would you rather take when it comes to cycling? Link from a fashion blog’s page that talks about cycling wear? That’s not perfect, but a lot better. Of course, any backlink, especially from a good quality website matters, but they don’t all “weigh” the same.
3.1. Hyperlink anchor text
By hyperlink text, or anchor text, this is meant:
<a href=”https://www.domain.com/page/”>Anchor text</a>Imagine a link to this page on another website. What should that link look like?
- Good post on backlinks
- Or: Bad post on backlinks
- Or perhaps: New Star Wars movie review?
Search engines assume that backlinks are created by humans and that they understood the contents of the page. This is why the contents of anchor text in backlinks are important. Pay attention to this when posting links to your content on social networks and forums. You can’t, of course, affect how others will link to your articles, but if you provide good titles (that aren’t too long), it might do the trick.
3.2. Nofollow and do follow backlinks
Nofollow links are those that include an instruction to search engines to not follow the link and not “see” what is on the linked page. As such, they carry a lot less “weight” (bring less benefit to domain authority) than do follow links who don’t prevent search engines from following them. Nofollow links are usually referred to as “NF“, while do follow are referred to as “DF“.
Here’s an example of a nofollow link HTML code:
<a href=”https://www.domain.com/page/” rel=”nofollow”>Anchor text</a>To website visitors it looks the same as any other link, but search engines will respect the part that says rel=”nofollow”.
Nofollow backlinks are not completely useless, since they do point people to your web pages, so even though they don’t provide any direct ranking benefits, perhaps those people will link to your site. Also, even a nofollow link on a page that has lots of visitors and has relevant content might just get people to keep visiting your site.
When you are making links, it is recommended to have links to paid adverts marked as NF, while all the others should be of DF type. If you make DF links to good quality content (as “sources”, or explanations of certain terms), it might even help your pages’ ranking. Search engines value content, so a good quality article that links to other good quality content relevant to the topic could be ranked higher than a similar article without the (external) links. It again boils down to the quality of content you offer to visitors.
Many forums set all the links as NF, in order to discourage users from posting link spam. This is not the best policy in my opinion, but perhaps necessary if there are not enough moderators. Some even completely forbid posting links to one’s own content, which is also wrong, but necessary for forums that attract too many spamers. WebHostingTalk forum is a good example. In fact, this entire post was started after I read a post about domain redirections effect on SEO on that forum. I would normally just link to this post as a reply, but I’m afraid that abandoning the strict linking policy would have that forum piled up with spam and hence useless to any members/visitors. On a note of NF links, it would be great if I could post a link, even a NF one, instead of none at all.
Advantage of NF links, if they are of good quality, is that they still provide more brand / domain recognition.
DF links are golden – since they bring better search engine ranking – if they are of good quality (relevant).
4. 301 redirections (permanent) and SEO
I wrote a separate post explaining 301 redirections. Here I’ll discuss those only in terms of SEO and website SERP positioning. That is: “what if I buy an existing domain and redirect all traffic to my domain?” Or, similar: “if I alter all the pages to serve my content (without redirection)”.
Scenario 1
Best case scenario: if every page is redirected to a page with content that is similar enough, then search engines will probably figure that the website has been migrated to a new domain. So you get to keep most of the old domain’s authority and page ranking.
Similar goes for editing page contents, without any redirects.
I have done both in the past, more than once and can confirm that it works.
Scenario 2
What if I redirect all the pages (entire old domain) to a new domain website starting page? If the old and the new website have similar content, visitors will be redirected to the new website, but not on the page they were looking for. They will probably not be thrilled. As far as search engines are concerned, the new domain remains ranked as it was before. While the old domain will loose rating, since all the pages (and backlinks) will lead to one page of a new domain website.
Example: mxroute.io now redirects to mailchannels.com – both offering email services, with mxroute.io bought out by MailChannels.
Source: gsqi.com/marketing-blog/redirects-less-relevant-pages-soft-404s/
If websites are with different topics, look at the next scenario.
Scenario 3
Redirects to a new domain website starting page, or particular pages on a new domain website, that has completely different content (even worse if it’s a completely different topic).
Example: I google for “stage makeup”, click on a search results page link and it redirects me to a website offering email hosting. I would feel cheated. Neither visitors, nor the search engines like this.
I haven’t tested if this is really harmful for rating – any links with tests are more than welcome. Still, I’d be amazed if it wasn’t.
5. Common SEO mistakes
Now I’ll briefly discuss common mistakes and misconceptions when it comes to SEO and (back)linking.
5.1. Too much worrying about “the keywords”
Page titles and link anchor text should relay what the (linked) page contents are about. If you want to sell email hosting service and write a page about email hosting, then sure, it’s good for a title and anchor text. However, if you write about email setup in cPanel, don’t title, or link to it using “email hosting”. It is deceptive. Both your visitors and search engines don’t like being fooled.
The trap most people fall into is worrying to much about keywords, not about explaining the topic properly, giving the reader a good quality content. The proper frame of mind is not “how can I include keywords?”, but:
“How I would like to have had this explained to me when I didn’t know anything about it?”
“What kind of content would I have found helpful?”
Find a good novice and ask them to review your content. Do they find it simple and easy to follow? Do they have any doubts, or questions? How could it be improved?
Don’t force any keywords, not in the titles, links, nor content itself. It does more harm than good.
Huge help with avoiding these mistakes can be provided by The SEO Framework (TSF) WordPress plugin – the best SEO plugin in my experience. Thanks to its “Focus” extension, which comes with the paid plugin version.
5.2. Backlink spaming
If you use your website link in a signature, search engines will usually recognize it as a signature and not put any weight on it.
On the other hand, if you post links everywhere, even when they are not relevant, this will be recognized as spam and penalized – sooner rather than later.
5.3. Buying backlinks, website directory listings
There are free website directory listings, where you can add your website and a short description of what it is about. Search engines know that these are practically Internet phonebooks, so these backlinks have no weight whatsoever.
Worse is with those who are asking you to pay them so they can post links to your websites “everywhere”. This is often achieved using a large network of dummy sites, used only for such purposes. It is considered trying to trick search engines and thus penalized.
On this topic you can read my post: SEO done wrongly.
6. Conclusion and sources
In the long run, the only efficient way for achieving high ranking is good content. There are no shortcuts, no replacements for it. Good backlink strategy (and offsite SEO in general) is only a way to make the ranking that your content objectively deserves come sooner.
Now, it is said that people like books where writers put in a nice way that what the people are already thinking. That might as well be the case with me and NeilPatel’s SEO website. Of many websites and texts (and people who are making a living of being “SEO ninjas”) that deal with SEO related topics, I find Neils to be the most common sense. In other words: I’m yet to find Neil’s post that contradicts what I know and have experienced.
Addition:
Any additions, corrections, or questions are welcome in the comment section below.

